Projects
This page gathers different projects using Ramses. Please contact Maxime Rey (maximerey.astro at gmail.com) if you wish to add your project here.
-

Space: Codes for Exascale
Ramses is part of the SPACE program, which aims to foster the reuse and sharing of algorithms and software components in the A&C application domain, addressing this action through co-design activities that bring together scientists, code developers, HPC experts, HW manufacturers and SW developers, advancing lighthouse exascale A&C applications, codes, services and know-how promoting the…
-

The AGORA Project
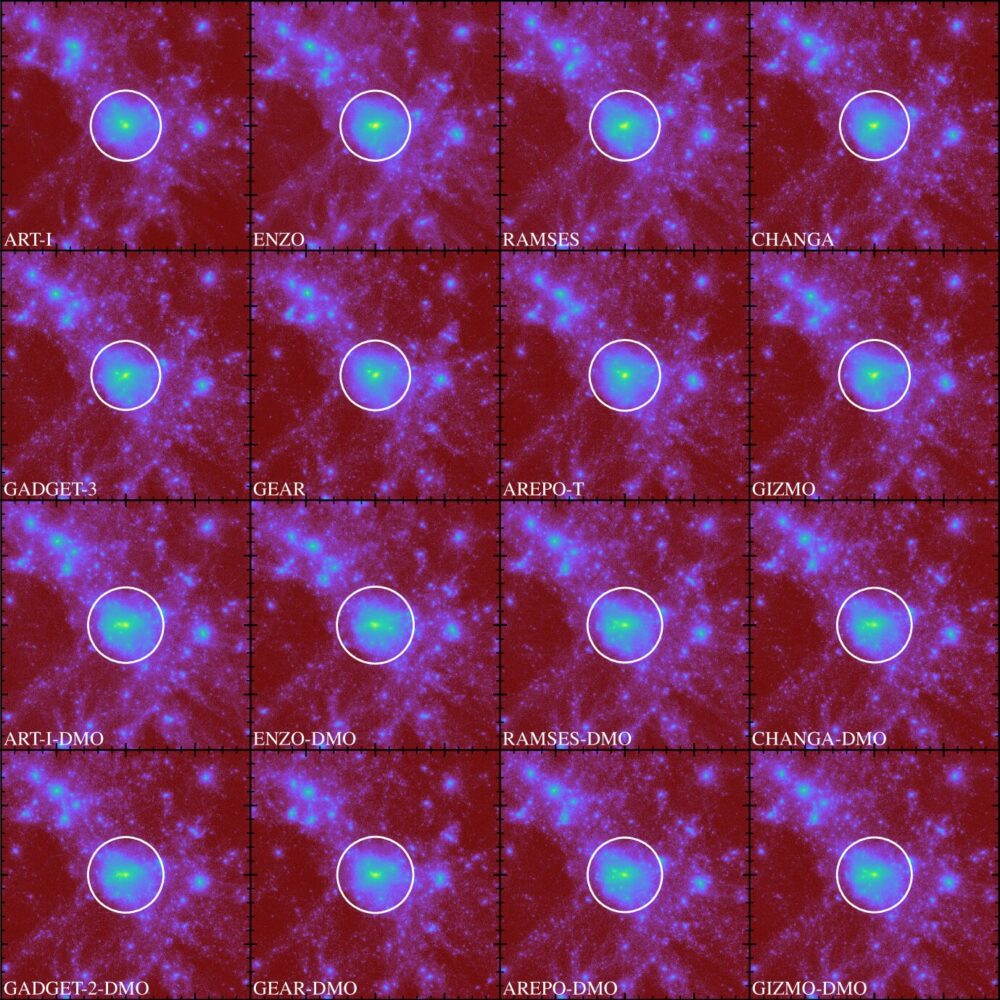
The Assembling Galaxies Of Resolved Anatomy (AGORA) project, introduced by Kim et al. (2014), aims to compare high-resolution galaxy formation simulations across different high-resolution numerical platforms. The numerical techniques and implementations used in this project include the smoothed particle hydrodynamics codes GADGET and GASOLINE, and the adaptive mesh refinement codes ART, ENZO, and RAMSES. The…
-

The Horizon Run 5
Horizon Run 5 (HR5, not to be mistaken with The Horizon Simulations), introduced by Lee et al. (2021) is a cosmological hydrodynamical simulation which captures the properties of the Universe on a Gpc scale while achieving a resolution of 1 kpc, aims to study the effect of large-scale perturbations on formation of galaxies and clusters.…
-

The DARWIN project
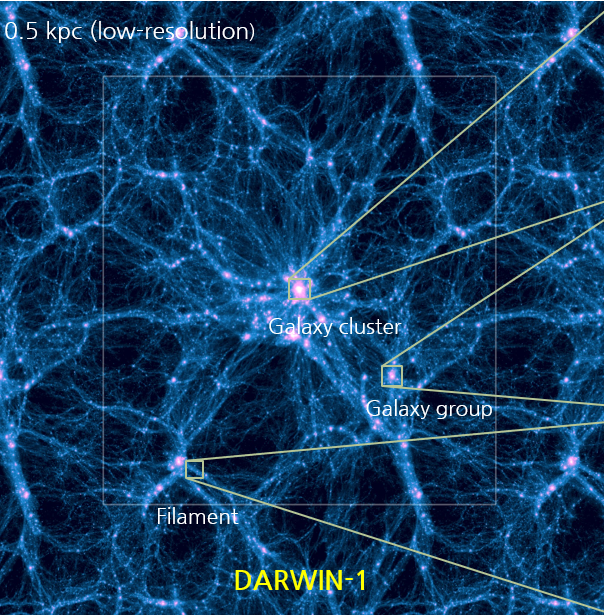
The DARWIN (DAzzling Realization of dWarf galaxies In the Next generation of cosmological hydrodynamic simulations) project aims at simulating the formation and evolution of dwarf galaxies, a key probe for testing both the galaxy formation models and standard cosmology, with a high resolution based on state-of-the-art physical ingredients in a cosmological context. The DARWIN project…
-

The EDGE project
The ‘Engineering Dwarfs at Galaxy Formation’s Edge’ (EDGE, Agertz et al. 2020) project aims to study the cosmological formation and evolution of the very smallest galaxies in the Universe. Website: https://edge-simulation.github.io/
-

The VINTERGATAN project
The VINTERGATAN project (Milky Way in Swedish, lit. The Winter Street) is a cosmological zoom simulation of a Milky Way-mass disc galaxy (Agertz et al. 2021). Website: https://people.astro.unistra.fr/f.renaud/vintergatan.php
Loading posts…